Deployment
Reading
Deployment
It is now time to deploy our application. For our application, we are going to
deploy to a service named Heroku. Heroku is a
Platform as a Service
company that provides hosting for a large range of application types.
It provides a free tier that allows our application and database to support a reasonable number of users and database size. It natively supports our Postgres database and has optional "buildpacks" (third party extensions) to host our C# application.
Git Based Deployment
One of Heroku's nicer features is sending code for hosting is a familiar task:
git push
Heroku will maintain a copy of your git repository and use a fresh git push to
determine that new code is ready for deployment to "production."
Getting setup
You should have a heroku account setup from the installation instructions. If not, create a heroku account now.
In your project, you will have a STUDENT.md file that includes instructions on
deployment. We'll repeat these steps here.
Deploying
These steps are run ONLY ONCE before you can deploy to heroku
NOTE: You must choose an app name that is unique across all of heroku. If you want to use a name that isn't available, try appending unique like
-sdgor-janedoereplacingjanedoewith your name.
heroku apps:create NAMEOFAPP- NOTE: replaceNAMEOFAPPwith something that is unique to your project.heroku buildpacks:add suncoast-devs/dotnetcore-buildpack
To Setup Secrets for Heroku
Heroku stores secrets in your environment variables. You can change these from
the command line or from your app's configuration on heroku.com
If you are using JWT tokens, you need to do the following:
heroku config:set JWT_KEY="MY RANDOM STRING OF LETTERS AND NUMBERS TO USE FOR A KEY"
If you are using a third-party API you can set any configuration as such:
heroku config:set THIRD_PARTY_KEY_NAME="THIRD PARTY KEY VALUE"
For instance, we might need these configurations. NOTE: use your real keys in
place of REPLACE-THIS
git push heroku HEAD:main
This command will push your code JUST to Heroku for hosting. This means when
you make a change, you should push to GitHub as normal (e.g. git push)
and also to Heroku (e.g. git push heroku HEAD:main).
You will notice that after the typical messages you get from a git push, your
terminal will show more messages from Heroku. A typical
git push heroku HEAD:main will look something like the following. (NOTE: The
specific numbers for your application will be different than shown here)
To Copy Your Local Database to Heroku
Heroku maintains its own copy of a database for your hosted application. That
means that all of the local data you have won't be live on your site. You can
take all the data in your local database and upload that to your Heroku copy of
the database. See the instructions in the
Heroku Quick Reference Guide to learn
how to Push a copy of your local database to Heroku
To Deploy Updates to Heroku
git push heroku HEAD:main
To Open Your Deployed Application
heroku open
To Setup Continuous Deployment
Continuous deployment will update your code on Heroku every time you push. You may choose to enable this mode of deploying to Heroku. However, you should know that there is a limit to the number of times you can deploy per day this way. You may only want to set this up if you are pushing code to Github infrequently.
- Visit heroku.com and go to the configuration page for your app
- Choose the
deploytab - Select
githubas the deployment method.
- Select
Connect to Github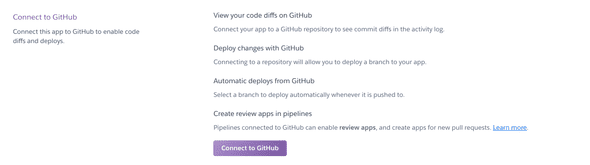
- Browse for your repository
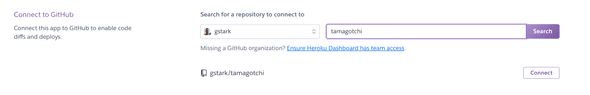
- Connect to your repository

- Enable automatic deploys
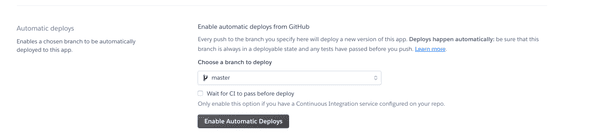
Viewing Logs When Something Breaks
Unlike your local environment, you won't be able to see any errors in your
application. Heroku gives you a way to view the logs (or output) from your
application.
The command comes in two modes:
The version with --tail will show you the output of your code until you press
Control-C. Logs with tailing are useful when you have an error when you load a
page in your application.